As medical science continues to advance, anti-aging treatments have naturally become more diverse, giving consumers a wider range of options than ever before. Procedures such as fillers, botulinum toxin injections, and laser treatments have become increasingly specialized—and, like all trends, they evolve with time. In the past, dermal fillers were the go-to choice for restoring facial volume. More recently, collagen-stimulating injections have gained popularity.
Now, it may be time to remember the next key concept in addressing skin concerns: stem cells. A topic drawing significant attention from both the medical and beauty industries, stem cells are the subject of ongoing and extensive research. While the term itself is familiar to many, few truly understand what stem cells are—or how they are being applied in anti-aging treatments.
Let’s take a closer look at what stem cells are and explore how this fascinating area of medicine is shaping the future of anti-aging care.

The human body maintains balance through the continuous cycle of cellular renewal—billions of cells are created and eliminated every day. At the core of this ongoing process are stem cells, which serve as the source of cellular regeneration. They function as the foundational cells that support tissues throughout the body, from the nervous system, skin, muscles, and bones to the blood, enabling repair and recovery. This is the fundamental nature of stem cells.
What Are Stem Cells?
The defining characteristic of stem cells is their ability to differentiate into multiple types of cells—such as nerve cells, muscle cells, and blood cells—a property known as multipotency. This capacity is what allows stem cells to play a critical role in repairing damaged tissues and, potentially, in the formation of new organs.
In addition, stem cells possess a remarkable ability known as self-renewal. They can replicate themselves indefinitely without differentiating, producing identical stem cells in the same undifferentiated state. This property enables stem cells to maintain a stable population within the body and to function as a continuous cellular reservoir.
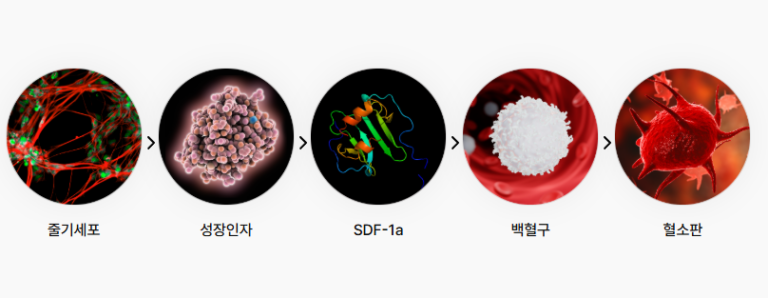
Are There Different Types of Stem Cells?
Stem cells are broadly classified into two main categories: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells possess exceptional differentiation and proliferative capacity, giving them significant potential in the treatment of various diseases. However, because they are derived from fertilized embryos, their use raises ethical concerns. In addition, their pluripotent nature—the ability to differentiate into virtually any cell type in the body—also carries a risk of uncontrolled cell growth, including tumor formation.
In contrast, adult stem cells are already present in the body during fetal development, infancy, and adulthood. They can be found in a variety of tissues, including bone marrow, blood, adipose tissue, and the nervous system. Unlike embryonic stem cells, which can differentiate into all cell types, adult stem cells have a more limited differentiation capacity and can develop only into specific lineages of cells.
Because adult stem cells are obtained from fully developed individuals, their use does not involve embryo destruction and therefore avoids ethical controversy. Moreover, when a patient’s own cells are used, the risk of immune rejection is significantly reduced. For these reasons, adult stem cells are currently the most widely studied and utilized in both research and clinical applications—and the stem cells used in dermatologic treatments fall into this category.
How Are Adult Stem Cells Used for Skin Health?
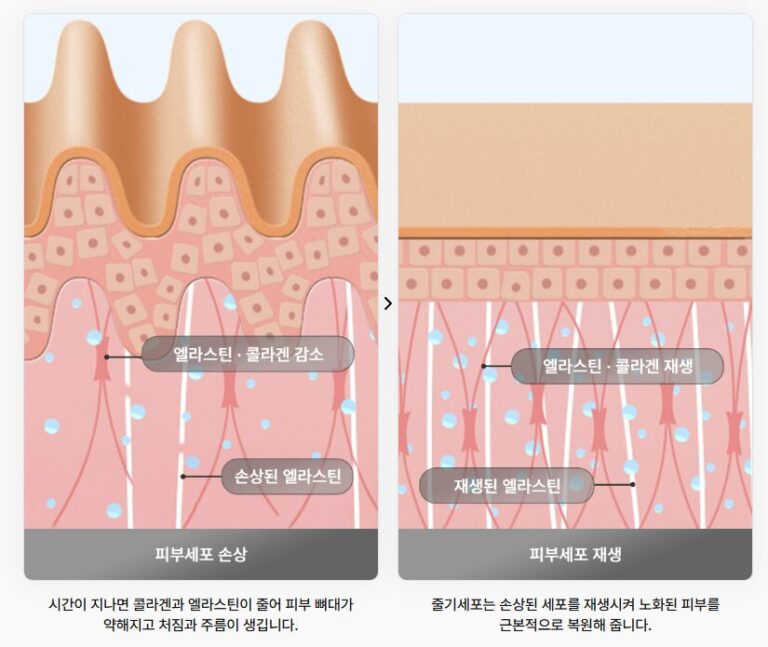
Cells in the human body are continuously renewed through a process in which aging cells are replaced with newly generated tissue. Adult stem cells play a central role in this process. By replacing damaged cells and generating new ones, they contribute significantly to tissue repair and regeneration—making them particularly effective in addressing skin aging and damage.
As aged or damaged cells are renewed, improvements in skin regeneration, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction may follow, making adult stem cells well suited for anti-aging applications. Unlike dermal fillers, which primarily focus on restoring volume, stem cell–based approaches aim to improve the overall skin environment and support long-term skin health.
As mentioned earlier, adult stem cells can be harvested from relatively accessible tissues such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, and blood. In dermatologic practice, blood-derived stem cells are commonly used due to the relative ease and safety of blood collection.
Stem Cell Injection Methods and Their Effects
Intravenous Stem Cell Therapy
Intravenous stem cell therapy involves administering stem cells—isolated from blood—into a vein along with an IV infusion. One of the key characteristics of stem cells is their homing effect, meaning that once introduced into the bloodstream, they circulate throughout the body and tend to migrate toward areas of injury or inflammation.
Through this systemic circulation, intravenous administration may support the recovery of underlying conditions that patients may not have been consciously aware of. As a result, this approach is often viewed not only as a cosmetic treatment, but as a more comprehensive method of health and wellness support beyond external appearance.
Potential Effects of Intravenous Stem Cell Therapy
Intravenous stem cell therapy is commonly used with the goal of supporting overall health and anti-aging, particularly in cases involving chronic fatigue, reduced immune function, age-related decline in physical performance, vascular health, and the management of inflammatory conditions.
It is also sought by individuals with persistent skin concerns—such as facial redness, recurrent breakouts, psoriasis, or atopic dermatitis—that are often considered difficult to manage. In these cases, the focus is less on immediate aesthetic improvement and more on systemic anti-aging and whole-body balance.
Stem Cell Skin Injections
Stem cell skin injections involve delivering stem cells directly into the dermal layer using an injection-based technique designed to provide localized effects on the skin. To minimize cell damage, a blunt, larger-gauge cannula is used to gently place the stem cells deep within the dermis.
Because stem cells are administered precisely to areas where anti-aging support is needed, this method allows for a more targeted and localized approach compared to intravenous administration, which distributes cells systemically throughout the body.
Potential Effects of Stem Cell Skin Injections
Once introduced into the dermal layer, stem cells may support the stimulation of collagen and elastin production. Collagen and elastin are essential structural proteins that help maintain skin firmness and play a key role in the formation of sagging and wrinkles.
Stem cells may also support the formation of new blood vessels, helping to improve nutrient delivery within the skin. As a result, improvements in skin tone clarity and texture smoothness may be observed. This approach focuses more directly on enhancing the skin’s internal environment and supporting regenerative processes.
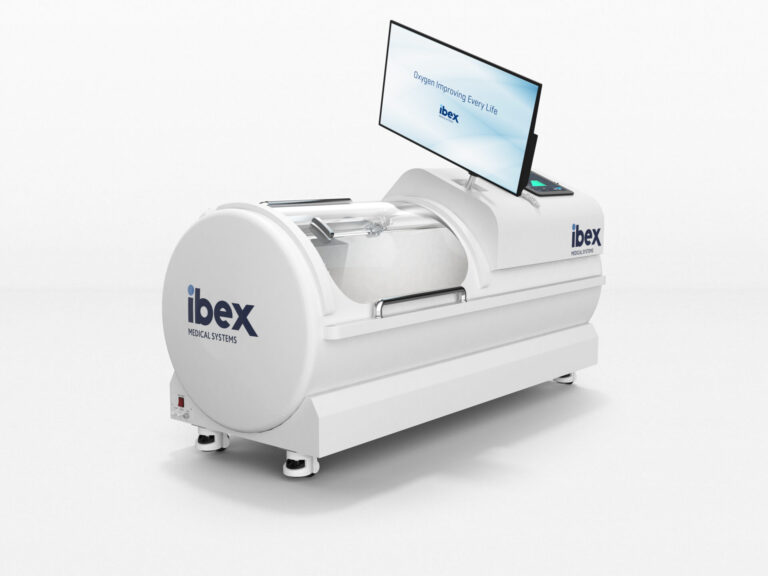
How to Enhance the Effects of Stem Cell Treatments: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves lying inside a pressurized chamber while breathing 100% pure oxygen for approximately one hour. The treatment is conducted at pressures of about 2 to 3 atmospheres, comparable to the pressure experienced at a depth of roughly 10–15 meters (30–50 feet) underwater.
Under normal atmospheric conditions, oxygen is primarily transported by binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells.

When undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the increased atmospheric pressure allows oxygen to dissolve directly into the blood plasma and circulate throughout the body. This enables high concentrations of oxygen to reach tissues and areas of injury that are typically difficult to oxygenate. Adequate oxygen delivery is associated with enhanced cellular regenerative activity and may support faster recovery of damaged tissue and wounds.
In addition, increased oxygen availability may help inhibit the growth of inflammation-causing bacteria, enhance the bactericidal function of white blood cells, and support the management of infection. Reduction of tissue swelling has also been reported in association with hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
When hyperbaric oxygen therapy is combined with stem cell–based treatments, it may further support stem cell homing and engraftment efficiency. Taking these potential benefits into consideration, selecting a clinic that offers stem cell injections and hyperbaric oxygen therapy as an integrated program—such as VOS Dermatology—can be a practical and comprehensive approach.
Stem Cell Injection Procedure and Treatment Duration
One of the reasons stem cell injection therapies have gained increasing attention is the relative simplicity of the procedure. Treatments that require prolonged downtime and delay return to daily activities tend to be less appealing in today’s fast-paced environment. In contrast, the streamlined process and minimal recovery time are considered key advantages of stem cell injections.
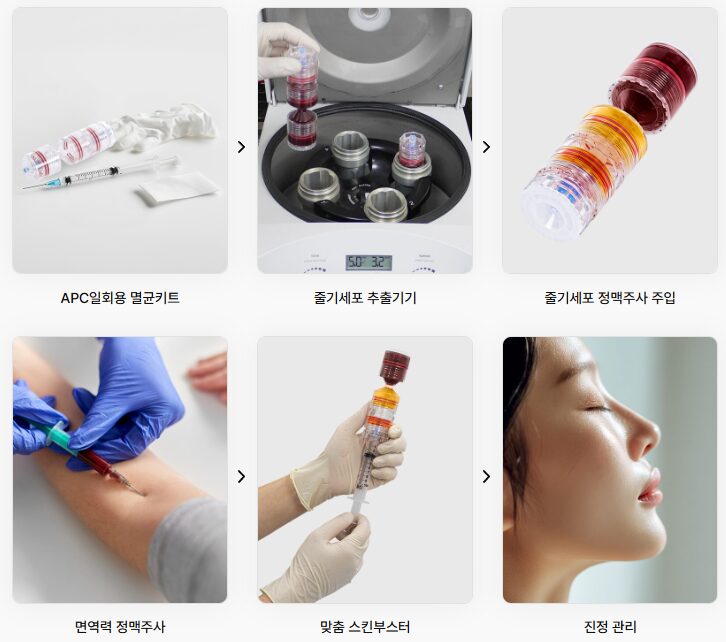
The procedure begins with blood collection for stem cell extraction. The collected blood is then processed using centrifugation to isolate and concentrate stem cells, a step that typically takes approximately 1 to 2 hours.
Following preparation, intravenous administration generally requires about one hour, while skin (dermal) injections take approximately 30 minutes.
After the procedure, hospitalization is not required. Patients are usually observed briefly for recovery and are able to return home the same day.
Pain and Potential Side Effects of Stem Cell Skin Injections
Concerns about pain associated with stem cell skin injections are generally minimal. While some discomfort may be experienced during the procedure, topical anesthetic cream is typically sufficient for pain control. Compared to skin booster injections such as polynucleotide-based treatments (e.g., Rejuran), stem cell skin injections are often perceived as less uncomfortable.
Pain sensitivity varies from person to person. For patients who are particularly sensitive or anxious about discomfort, the procedure may be performed under sedation anesthesia following consultation with the practitioner.
Bruising and swelling depend on individual skin type and response, but pronounced swelling or raised bumps are uncommon. Most temporary reactions, including mild redness, bruising, or swelling, tend to resolve within 2 to 3 days. In most cases, any residual redness or bruising can be easily concealed with makeup and typically subsides within one week.
For reference, intravenous stem cell injections involve little to no downtime. Similar to standard IV infusions, patients are usually able to resume normal daily activities immediately after treatment.
Because stem cell treatments commonly utilize the patient’s own cells, the risk of immune rejection is considered low, making this approach relatively safe when performed under appropriate medical supervision.